VR Patient Education: Overcoming Challenges and Opportunities
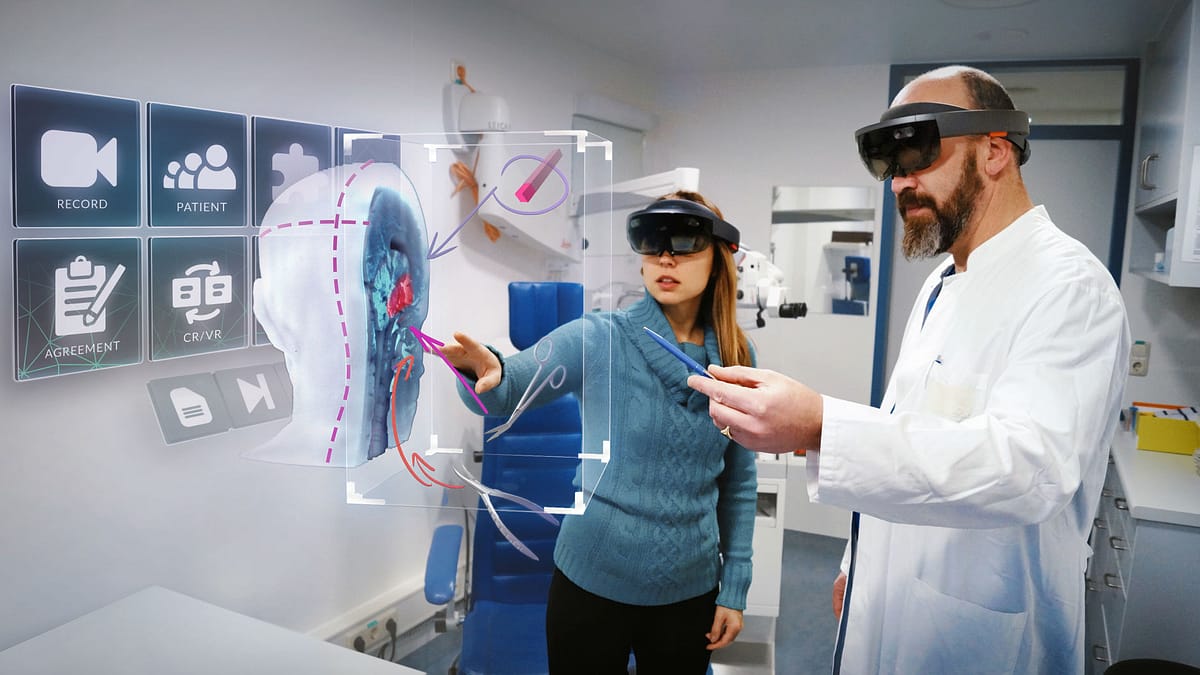
Virtual Reality (VR) technology has revolutionized various industries, including healthcare. In patient education, VR offers a dynamic platform for delivering immersive and interactive experiences. Understanding the fundamentals of VR and its integration into healthcare settings is crucial for maximizing its potential.
Understanding Virtual Reality (VR)
VR refers to a simulated environment created using computer technology, where users can interact with digital objects and experience sensory feedback. Unlike traditional methods of patient education, which often rely on static images or videos, VR provides a fully immersive experience, allowing users to explore medical concepts in a virtual space.
Importance of Patient Education
Patient education plays a vital role in healthcare by empowering individuals to make informed decisions about their health and treatment options. Well-informed patients are more likely to adhere to treatment plans, manage chronic conditions effectively, and experience better health outcomes overall. VR presents an innovative approach to patient education, offering engaging and memorable learning experiences.
Integration of VR in Healthcare
The integration of VR technology in healthcare settings has expanded rapidly in recent years. From medical training simulations to therapeutic interventions, VR applications in healthcare are diverse and impactful. In patient education, VR offers a range of benefits, including an improved understanding of medical procedures, enhanced patient engagement, and opportunities for personalized learning experiences.
Challenges Faced in Implementing VR Patient Education
While VR holds tremendous potential for transforming patient education, several challenges must be addressed to ensure successful implementation and adoption.
Technical Barriers
- Hardware Limitations
VR hardware, such as headsets and controllers, can be expensive and require significant processing power to operate effectively. Compatibility issues between different VR devices and software platforms may also pose challenges for healthcare providers seeking to integrate VR into patient education programs.
- Software Compatibility
Choosing the right software app for VR patient education can be daunting. Healthcare organizations must ensure that the software they select aligns with their educational objectives, integrates seamlessly with existing systems, and meets regulatory requirements for data security and patient privacy.
Cost Constraints
- Initial Investment
The initial cost of implementing VR technology in healthcare settings can be prohibitive for some organizations. Expenses associated with purchasing hardware, developing customized content, and training staff members on VR use may strain limited budgets, especially for smaller clinics or nonprofit healthcare providers.
- Maintenance Expenses
In addition to upfront costs, ongoing maintenance and support expenses can add to the total cost of ownership for VR systems. Regular software updates, hardware maintenance, and technical support services are essential for ensuring the reliability and functionality of VR equipment in healthcare environments.
User Acceptance
- Resistance to Change
Introducing new technologies like VR into healthcare settings may encounter resistance from both patients and healthcare professionals. Skepticism about the effectiveness of VR for patient education, concerns about usability and comfort, and fear of technology-related errors or malfunctions may hinder adoption efforts.
- Training Requirements
Effective use of VR technology requires adequate training and support for both patients and healthcare providers. Educating users on how to navigate VR environments, interact with virtual objects, and troubleshoot common issues is essential for maximizing the benefits of VR patient education programs.
Ethical Considerations
- Patient Privacy
Maintaining patient privacy and confidentiality is a paramount concern in healthcare, particularly when implementing technologies like VR that involve the collection and storage of sensitive data. Healthcare organizations must adhere to strict regulatory guidelines and industry standards for protecting patient information in VR environments.
- Informed Consent
Obtaining informed consent from patients participating in VR-based educational activities is essential for respecting their autonomy and rights. Patients should be fully informed about the nature of the VR experience, its potential risks and benefits, and their rights regarding the use of their personal health information.
Opportunities Offered by VR in Patient Education
Despite the challenges, VR presents numerous opportunities for enhancing patient education and improving healthcare outcomes.
Enhanced Learning Experience
- Immersive Simulations
VR allows patients to immerse themselves in realistic simulations of medical procedures, anatomical structures, and healthcare environments. By experiencing these simulations firsthand, patients gain a deeper understanding of complex medical concepts and procedures.
- Interactive Modules
Interactive VR modules engage patients in active learning experiences, where they can manipulate virtual objects, participate in guided exercises, and receive immediate feedback on their actions. This hands-on approach to learning fosters curiosity, exploration, and retention of information.
Increased Patient Engagement
- Personalized Content Delivery
VR technology enables healthcare providers to customize educational content to meet the unique needs and preferences of individual patients. By tailoring VR experiences to address specific learning objectives, patients are more likely to stay engaged and motivated throughout the educational process.
- Gamification Elements
Incorporating gamification elements into VR patient education programs can make learning more enjoyable and rewarding. By earning points, completing challenges, and unlocking achievements, patients are incentivized to actively participate in their educational journey and track their progress over time.
Accessibility Improvements
- Remote Education Options
VR technology offers the potential for remote patient education, allowing individuals to access educational content from the comfort of their own homes. This is particularly beneficial for patients with mobility limitations, those residing in rural or underserved areas, or individuals who prefer the convenience of learning remotely. By eliminating geographical barriers, VR expands access to high-quality healthcare education and empowers patients to take control of their health regardless of their location.
- Overcoming Language Barriers
Language barriers can hinder effective communication between healthcare providers and patients, leading to misunderstandings and suboptimal care. VR patient education programs can overcome these language barriers by providing multilingual content and interactive translation features. Patients can select their preferred language within the VR interface, ensuring that educational materials are accessible to individuals from diverse linguistic backgrounds.
Empowerment of Healthcare Providers
- Better Communication Tools
VR technology enhances communication between healthcare providers and patients by facilitating immersive interactions and visual demonstrations. Healthcare professionals can use VR simulations to explain complex medical concepts, demonstrate treatment procedures, and address patient concerns clearly and engagingly. By incorporating visual aids and interactive elements, VR fosters meaningful dialogue and strengthens the patient-provider relationship.
- Efficient Training Methods
In addition to patient education, VR is a valuable tool for training healthcare professionals in various clinical skills and procedures. Simulation-based training allows medical students, residents, and practicing clinicians to practice hands-on skills in a safe and controlled environment. From surgical simulations to emergency response drills, VR training programs enable healthcare providers to refine their skills, improve patient outcomes, and enhance the overall quality of care.
Future Trends and Innovations in VR Patient Education
The future of VR patient education holds exciting possibilities, with ongoing advancements in technology, research, and clinical practice driving innovation and expansion in this field.
Advancements in VR Technology
- Higher Resolution Displays
As VR hardware continues to evolve, we can expect to see improvements in display resolution, refresh rates, and field of view. Higher-resolution displays enhance visual clarity and realism in VR simulations, making educational content more engaging and immersive for users. By minimizing visual artifacts and screen-door effects, advanced VR displays deliver a more lifelike experience and facilitate deeper learning.
- Wireless Connectivity
Wireless VR headsets offer greater freedom of movement and flexibility for users, eliminating the need for tethered connections to external devices. This wireless functionality enhances comfort and convenience during VR experiences, allowing patients to move freely within virtual environments without being restricted by cables or wires. By untethering VR technology, wireless headsets promote mobility and accessibility in patient education settings.
Integration with Artificial Intelligence
- Personalized Learning Algorithms
AI-driven algorithms can analyze user interactions and preferences within VR environments to personalize educational content and adapt learning experiences in real-time. By tracking user behavior, cognitive responses, and learning outcomes, AI algorithms can tailor VR simulations to match individual learning styles, pace, and preferences. This personalized approach to education maximizes engagement, retention, and knowledge transfer for patients of all ages and abilities.
- Adaptive Feedback Systems
Incorporating adaptive feedback systems into VR patient education programs enables real-time assessment and reinforcement of learning objectives. These systems use machine learning algorithms to provide immediate feedback, corrective guidance, and adaptive challenges based on user performance within VR simulations. By offering tailored feedback and support, adaptive systems enhance learning outcomes, promote skill acquisition, and foster self-directed learning in patients.
Expansion into Telemedicine
- Virtual Consultations
VR technology facilitates virtual consultations between patients and healthcare providers, enabling remote access to medical expertise and advice. Through VR telemedicine platforms, patients can interact with clinicians in immersive virtual environments, discuss treatment options, and receive personalized recommendations without the need for in-person appointments. This virtual care delivery model increases access to healthcare services, reduces travel burdens, and enhances patient-provider communication.
- Remote Monitoring
In addition to consultations, VR enables remote monitoring of patients’ health status and adherence to treatment plans. Wearable VR devices equipped with sensors and biometric trackers can collect real-time health data, such as vital signs, movement patterns, and medication adherence. Healthcare providers can remotely monitor patients’ progress, identify potential health issues, and intervene proactively to prevent complications. This remote monitoring capability improves patient outcomes, reduces hospital readmissions, and enhances overall healthcare efficiency.
Conclusion
In conclusion, virtual reality (VR) holds tremendous promise for transforming patient education and enhancing healthcare outcomes. Despite the challenges associated with implementing VR technology in clinical settings, the opportunities for improving patient engagement, increasing accessibility, and empowering healthcare providers are undeniable.
By addressing technical barriers, leveraging funding opportunities, investing in education and training programs, and complying with regulatory standards, healthcare organizations can overcome obstacles and unlock the full potential of VR in patient education. Embracing innovation, collaboration, and continuous improvement is key to realizing the vision of VR-enabled healthcare education that is immersive, interactive, and impactful.
Blog Categories
- Company News (33)
- Healthcare Operations (1)
- Industry News (19)
- Sales Enablement (2)
- Software Publishers (2)
- Virtual/Augmented Reality (2)